Key Takeaways
- Xanax addiction changes how the brain and nervous system function, leading to both mental and physical struggles.
- Long-term use of Xanax impacts memory, mood, coordination, and overall health.
- Professional addiction treatment is the safest path to recovery and lasting stability from Xanax addiction.
The Truth About Xanax Addiction
Xanax is often prescribed to ease anxiety or panic, but for many, it becomes more than just a short-term solution. People take it for relief from stress or racing thoughts, but over time, the body and mind begin to rely on it. What once felt helpful can turn into dependency, leading to serious effects on both physical and mental health. At Ocean Hills Recovery in Orange County, we want you to know recovery is possible. Our programs provide support, healing, and family-focused care to help you break free from xanax addiction.
What is Xanax?
Xanax is the brand name for alprazolam, a prescription medication in the benzodiazepine family. Doctors prescribe it for conditions like generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, or short-term anxiety relief. It works by enhancing the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a chemical messenger that slows down activity in the brain and nervous system.
While it can provide relief in the short term, Xanax has a high risk for drug abuse because tolerance and dependence can develop quickly. People may find themselves taking more than prescribed to feel the same calming effect, which sets the stage for addiction.
How Xanax Works in the Brain
Xanax interacts with gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors, which are responsible for slowing down activity in the central nervous system. By increasing the effects of GABA, Xanax reduces excessive brain activity and produces a calming effect that can temporarily relieve anxiety or panic symptoms.
While this effect may feel beneficial at first, repeated exposure alters the brain’s natural regulation of mood and stress. Over time, the brain adapts and begins to rely on Xanax to maintain balance. Without the drug, individuals may experience heightened anxiety, irritability, restlessness, or insomnia. These withdrawal symptoms often reinforce continued use, making it difficult to stop without professional support.
The Impact of Xanax on the Nervous System
The nervous system regulates both involuntary functions, such as breathing and heart rate, and voluntary actions like movement and coordination. Xanax slows communication between nerve cells by enhancing GABA activity, which decreases excitability throughout the system. This reduction in nervous system activity explains why the medication can ease panic symptoms and reduce physical tension.
However, frequent or excessive use disrupts normal function. Prolonged exposure can impair motor skills, slow reflexes, and reduce overall alertness. Individuals misusing Xanax may exhibit drowsiness, slurred speech, poor coordination, and an increased risk of accidents. Over time, these effects compromise not only daily functioning but also long-term neurological health.
Physical Effects of Long-Term Xanax Use
Long-term use of Xanax creates many physical changes that can harm daily health:
- Muscle weakness and fatigue
- Headaches and dizziness
- Stomach problems such as nausea or constipation
- Reduced coordination and balance
These effects may seem small at first but often grow worse as dependency develops. For many, stopping use without support can also create dangerous withdrawal symptoms, including seizures.
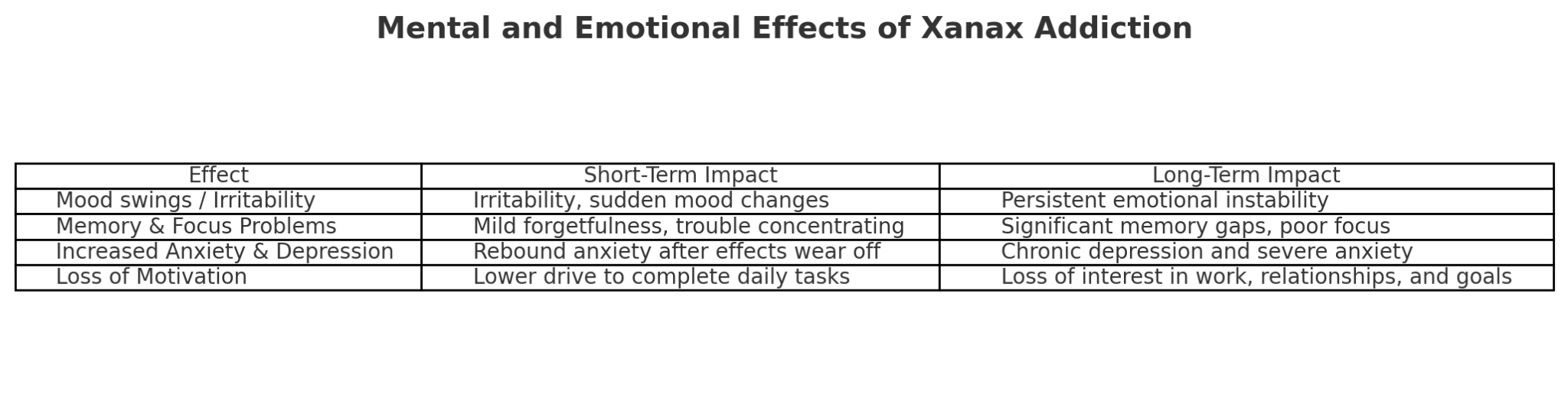
Mental and Emotional Effects of Xanax Addiction
The effects of xanax addiction extend beyond the physical body. Mental and emotional health often take the hardest hit. People may experience:
- Mood swings or irritability
- Memory problems and difficulty focusing
- Worsening anxiety and depression
- Loss of motivation
Because Xanax alters brain chemistry, people can feel trapped in a cycle where anxiety increases when they don’t take it, making them believe they need more.
Warning Signs Xanax Use Is Becoming Addiction
Recognizing early signs can help someone get support before dependency grows deeper. Warning signs include:
- Taking more than prescribed
- Doctor shopping to get extra prescriptions
- Using Xanax with alcohol or other drugs
- Struggling with daily tasks without it
- Withdrawal symptoms when missing doses
If you or someone you love shows these signs, it may be time to seek drug treatment.
Risks of Stopping Xanax Without Support
Quitting Xanax suddenly without medical help can be dangerous. The brain and body become dependent on the drug, and withdrawal can bring symptoms such as:
- Severe anxiety
- Shaking and sweating
- Insomnia
- Seizures
Because of these risks, it is safest to stop use with medical detox and structured addiction treatment at a center like Ocean Hills Recovery.
When Brain and Body Dependence Overlap
The hardest part of xanax addiction is how it affects both the brain and body at once. Emotional cravings mix with physical dependence, making it feel impossible to quit. This overlap keeps people stuck in addiction even when they want to stop.
Support from family, counseling, and professional detox care can break this cycle and give people the strength to heal.
Treatment Options for Xanax Addiction
At Ocean Hills Recovery, we provide safe, evidence-based addiction treatment programs for Xanax dependence. Options may include:
- Detox with medical supervision to reduce withdrawal risks
- Residential treatment for structured support in a safe setting
- Partial hospitalization programs for intensive day treatment
- Family programming to bring loved ones into the healing process
- 12-step recovery program to build connection and accountability
Every person’s experience is different, and treatment plans are built around the individual’s needs. Recovery is possible, and we believe no one should face addiction alone.
Get Xanax Help at Ocean Hills Recovery
Xanax may seem like an answer in the beginning, but over time it can trap the brain and body in dependence. Both physical health and emotional balance are at risk when addiction develops. If you or someone you love is struggling, you don’t have to go through it alone.
Call Ocean Hills Recovery today and take the first step toward safe, supportive addiction recovery. Our Orange County team is here to guide you toward healing with care and understanding.
FAQs
1. What organ is Xanax hard on?
Xanax is especially hard on the liver, since that’s where it is processed, but it also strains the brain and central nervous system.
2. Do side effects of Xanax go away?
Some mild side effects, like drowsiness or dizziness, may fade as the body adjusts. Long-term effects often continue until use is reduced or stopped.
3. How to get rid of alprazolam addiction?
The safest way is through medical detox and structured addiction treatment. Professional support helps manage withdrawal and build lasting recovery.
4. What are the side effects of alprazolam on the brain?
It can slow brain activity, impair memory and focus, and increase risks of anxiety or depression when dependence develops.
5. Can alprazolam cause cognitive decline?
Yes. Long-term misuse has been linked to memory loss, slower thinking, and reduced mental sharpness, especially in older adults.













